Information
| Partner: | FORTISS, MUNICH, GERMANY |
| Advanced Technology: | Framework for Distributed Industrial Automation & Control |
| Contact: | Dr. Holger Pfeifer |
| Email: | pfeifer@fortiss.org |
Framework for Distributed
Industrial Automation & Control
Today’s automation and control systems are mostly implemented according to a vendor specific dialect of the IEC 61131 standard. The different dialects make programs for programmable logic controllers (PLC) hardly portable between different PLCs. With its PLC centric design and its scan-based nature, the IEC 61131 standard already exceeds the needs of today’s automation systems. Therefore the same standardization group, originating IEC 61131, worked on a more flexible version, supporting distributed automation and control systems, the IEC 61499 standard.
IEC 61499 based systems follow an application centric design, which means that the application of the overall system is created at first and independent of the hardware. Each application is created by interconnecting the desired function blocks (FB) in terms of a function block network (FBN). The IEC 61499 standard extends the FB concept, already introduced within the IEC 61131 standard by an event interface, which allows an explicit definition of the execution order. This is required especially for distributed systems.
As soon as the hardware structure is known it can be added to a project’s system configuration and the already existing application can be distributed onto the available devices. The interoperability of devices from different vendors is one key feature postulated by the IEC 61499 standard. Also the portability of applications between different IEC 61499 engineering tools has been addressed by introducing an XML exchange format. Due to the definition of management commands different devices can be configured by different IEC 61499 engineering tools. The same commands can be used for online reconfiguration.
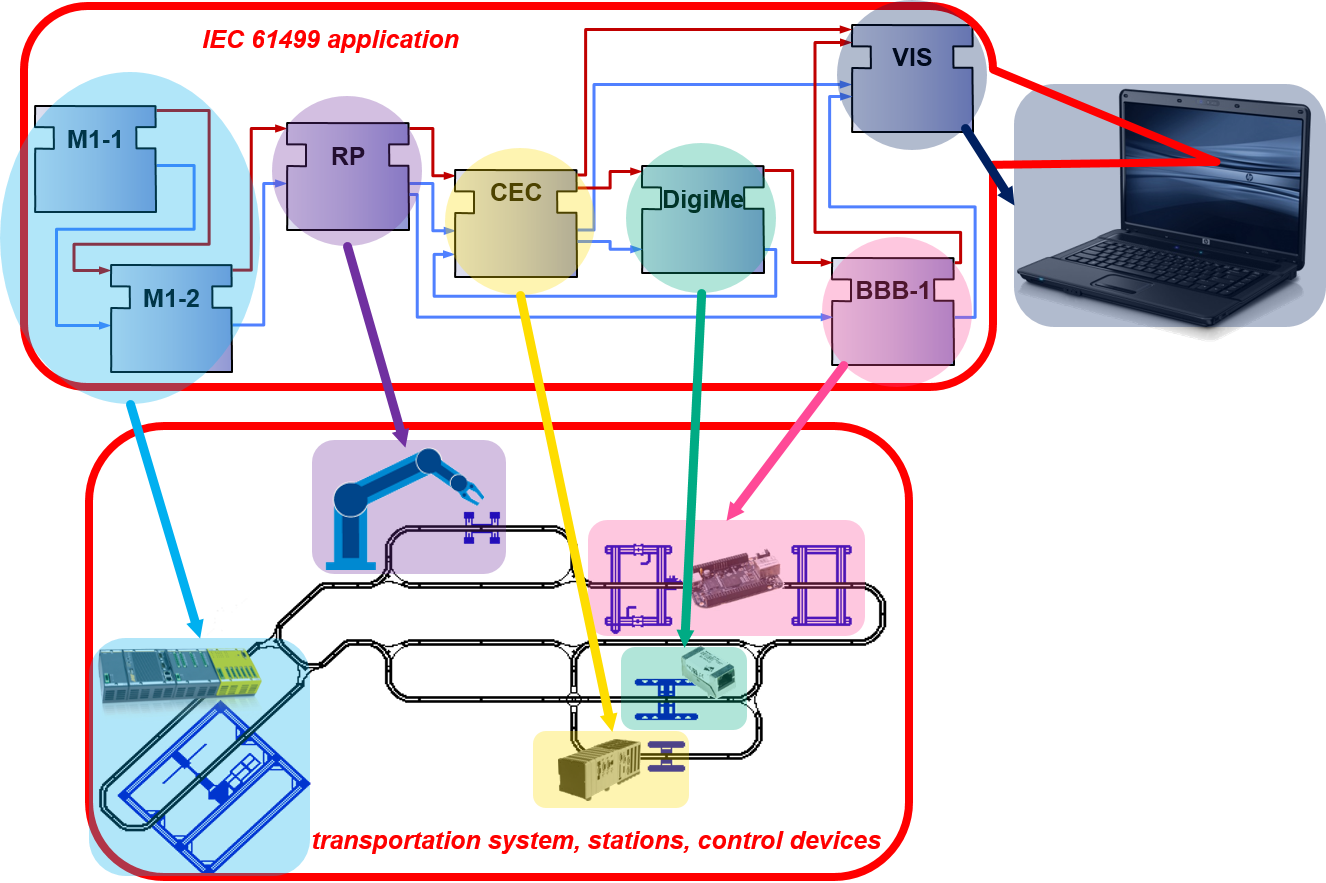
Eclipse 4diac™ implements the IEC 61499 standard and is intended for the programming of programmable logic controllers (PLCs) as well as small embedded control devices. 4diac is provided as open source software under EPL-1.0 and consists of two parts: forte (4diac-rte) and 4diac-ide.
- forte is a real-time capable IEC 61499 run-time, which operates on different hardware platforms. The hardware platforms reach from small embedded control devices up to PLCs. Currently supported hardware platforms comprise e.g. Weidmüller PLC, Wago PLC, Raspberry Pi, BeagleBone Black, or LEGO Mindstorms NXT. forte has been tested on e.g. Windows Cygwin on i386, ppc and xScale Linux on i386, ppc and xScale NetOS RTOS on IPC@chip and eCos on ARM7. It supports all IEC 61131-3 edition 2 elementary data-types, structures, and arrays. Applications can consist of any IEC 61499 element as basic function blocks, composite function blocks, service interface function blocks and adapters. Besides that forte provides a flexible and extendable communication infrastructure already providing a large set of protocols, e.g. MQTT, OPC UA, openPOWERLINK or EclipseSCADA.
- 4diac-ide is an extensible, Eclipse-based integrated development environment (IDE) for IEC 61499 compliant programs. It supports the modelling of distributed control software as well as the deployment to the various hardware devices. 4diac-ide makes it easy to create new applications in a modular way by reusing existing function blocks from standard libraries. The modelled applications can be deployed to IEC 61499 powered control devices. For testing, 4diac-ide provides monitoring and debugging facilities to “watch” events and data values during execution. One can also interact with the application by changing or forcing data to have certain values, and by triggering events.
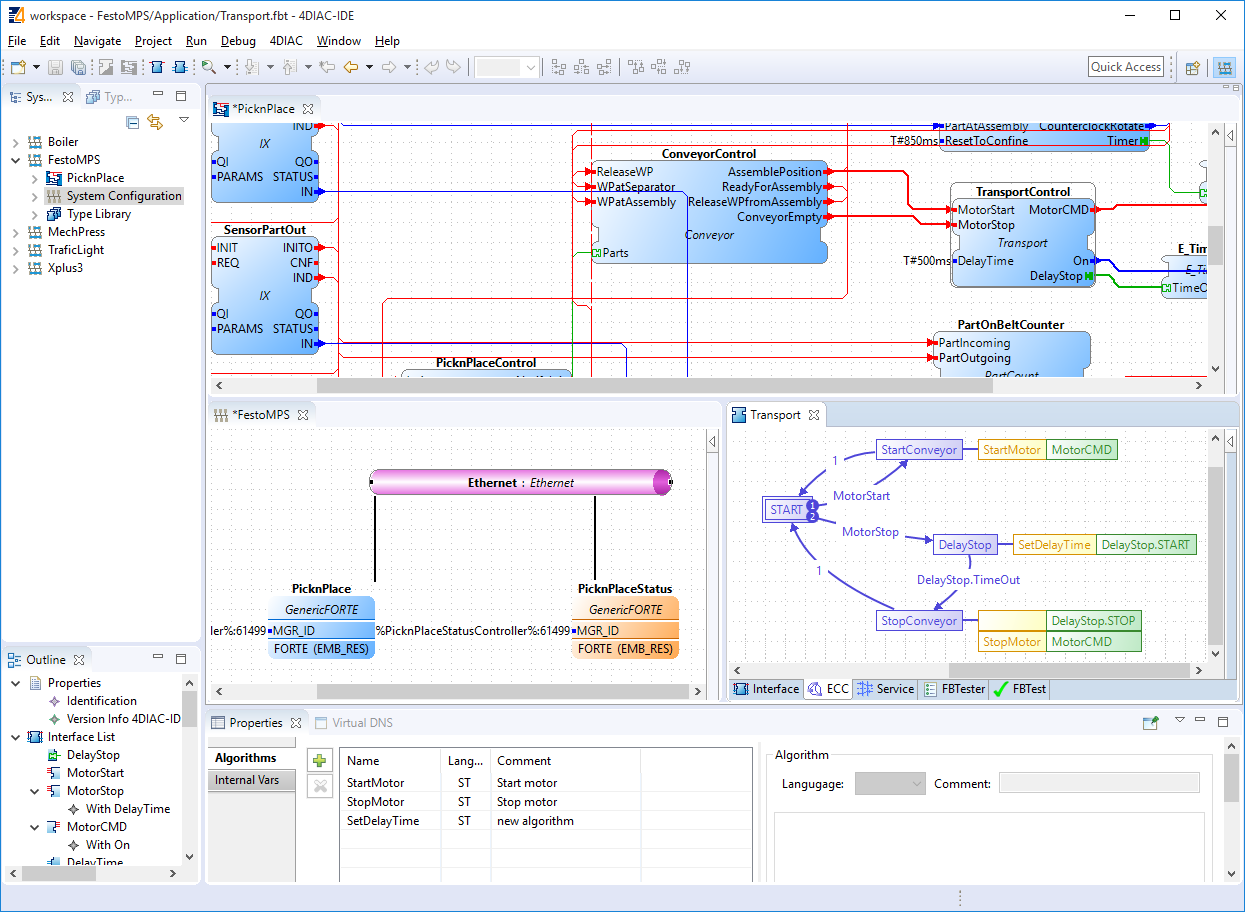
4diac has been evaluated by case studies of different organizations:
- The Profactor Case Study. Profactor is located in Steyr, Austria and is Austrian’s No. 1 in applied production research. As a private research company, it performs applied research across different disciplines to find solutions for the manufacturing industry. The Profactor case study employed the 4diac platform on a robotic arm application.
- The AIT Case Study. The AIT (Austrian Institute of Technology) is Austria’s largest non-university research institute, and among the European research institutes a specialist in the key infrastructure issues of the future. In this case study AIT examined the use of the 4diac platform in a smart grid laboratory.
- The ACIN Case Study. Vienna University of Technology – Automation and Control Institute (ACIN) performs research and education in the fields of distributed automation and control systems, as well as precision engineering, scientific instrumentation and process-measurement systems with focus on industrial relevant applications for industrial automation, production, and measurement systems. The ACIN case study allowed the Vienna Institute of Technology’s Automation and Control Institute to demonstrate the real time capability of the 4diac platform.
- Awite Bioenergie GmbH. Awite is a SME located near Munich and is specialist for gas analysis and desulfurization as well as the automation of the corresponding processes. Within their CPSE Labs Experiment they implemented an energy load management approach with 4diac. They summed up their results within a YouTube video.
For more info please contact
Dr. Holger Pfeifer
Email: pfeifer@fortiss.org


